Chemistry basics, SI units and chemical calculations, chemical concentration, equilibrium constant
과학/분석화학 2021. 2. 14. 16:46The scientific and international official unit is called the SI unit, or System International unit.
This was unified because of the confusion through the units, does, muscles, and chucks used in Korea in the past, and American miles, feet, and pounds, and European ounces.
Of course, the United States still exists as an officially unused country.
This SI unit basically has meter, kilogram, second, ampere, kelvin, candela (glossiness), mole, radian, etc.
There are also Si derived units with distinctive names, for example N Newton.
In order to derive by F, F=ma=kg(m/s^2)=kg*m/s^2
From then on, to explain the energy, F*m=kg*m^2/s^2=J
It can be said that all of these scientific units start with SI and are derived and become derived units.
This should be able to do chemical problems, chemical calculations.
You must be able to figure out how to find out the number of neurotransmitter molecules with an electrode, or how to count the number of electrons from the number of molecules.
Of course, I will present all the SI units and necessary conditions in the problem, but you have to practice a lot.
It is also necessary to calculate energy in watts, calculate that watt in horsepower, and calculate it in calories.
Chemical concentration is typically a molar concentration and a molar concentration.
The first thing to say is solutes and solvents.
Solute is a small number of species in solution and is a representative value.
Solvent is a number of chemical species in the solution, typically water and aqueous solution
There is also a foam concentration (F), which is called the molar concentration of a strong electrolyte, and if the mole of solute to be obtained is 0.01M, it is only 0.01F.
Molar concentration (M) is the number of moles of substance per liter of solution, which is M = number of moles of solute/liter of solution.
The molar concentration (m) represents the number of moles of a substance per kg of solvent, so that m = number of moles of solute/kg of solvent.
The difference between molar concentration and molar concentration is that molar concentration does not change with temperature.
This is because the volume of the solution changes with temperature (PV=nRT)
It is representative to find the molar concentration of salt in seawater to find this molar concentration and molar concentration.
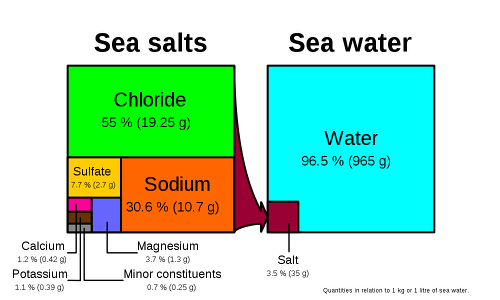
With this, you can prepare a solution and you must be able to calculate how much solute can be dissolved in a solvent to make a solution.
In addition, in order to prepare a solution of the desired molar concentration, the mass of the pure reagent is accurately measured and prepared in a volumetric flask. Here, miniscus should be expected.
Also, when you do this concentration calculation, you know that it is an equilibrium constant.
Equilibrium is the state that the system reaches when it has been waited long enough, and in chemistry, this long wait time reaches parallel within minutes.
Equilibrium constant K=([C]^c[D]^d)/([A]^a[B]^b)
If K>1, the equilibrium constant is greater than 1, the positive reaction is advantageous, and the equilibrium constant has no unit.
It can be said that it is used for acid base titration and precipitation reaction.
In addition, since the solvent concentratin of pure solid and liquid is 1, it is omitted.
'과학 > 분석화학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| General steps in chemical analysis (0) | 2021.02.14 |
|---|---|
| Analytical Chemistry, Chemical Analysis Process (0) | 2020.07.08 |
| Introduction to Analytical Chemistry, Examples of Analytical Chemistry (0) | 2020.07.08 |
| 산과 염기를 통한 적정(Titration) (0) | 2016.05.25 |
| Kjeldahl 질소 분석법(킬달 분석법, Nitrogen analysis) (1) | 2016.05.25 |