You can think of organic chemistry as a study that shows curiosity about organic compounds in living organisms.
Most organic compounds contain carbon, and as an example, the distribution of hair (protein), DNA, food, and medicine is very diverse.

In other words, it is a plant and animal, or a substance produced from plants and animals.
With a brief history of organic chemistry
Organic chemistry was established in the mid-1700s, and organic compounds obtained from plants and animals have a lower melting point than inorganic compounds, so they are difficult to decomposed, separate and purify.
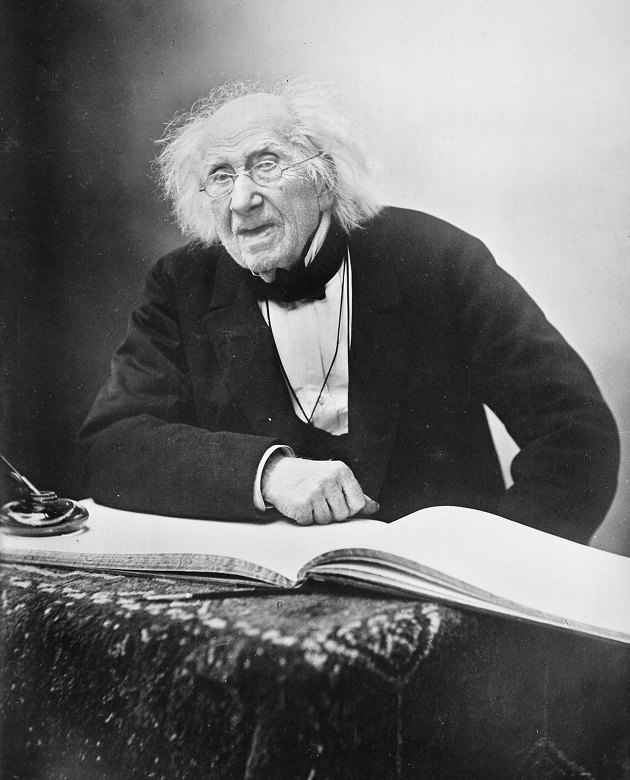

In 1816, Michel cherreul made a soap with an organic compound of animal fat and alkali, and then fatty acid, an organic compound, to refute the vitality that was popular at the time.
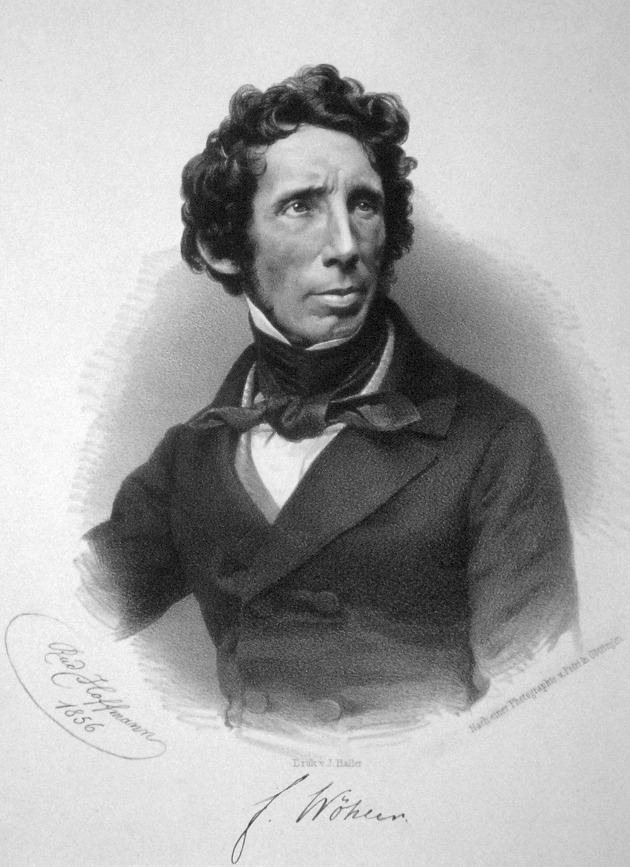

In 1828, Frledrich wohler extracts Urea, an organic compound, from human urine, which is an inorganic salt, completely eliminating vitality.
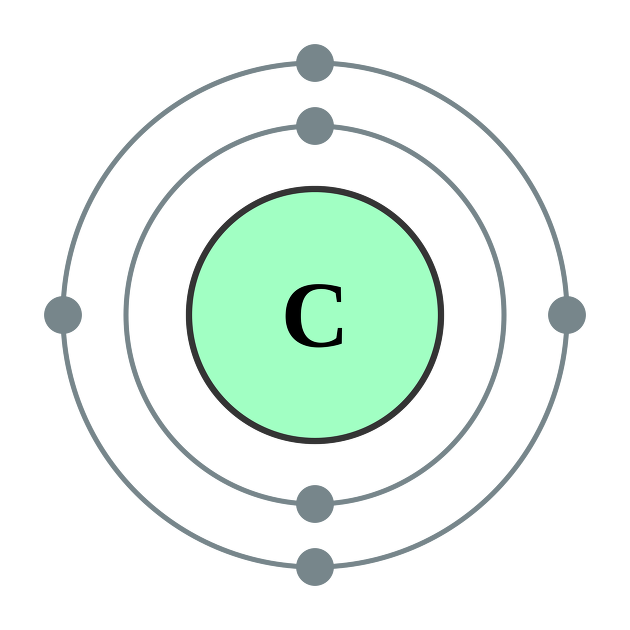
Carbon is the most important element in organic chemistry.
Carbon is more than 90% of most compounds and is typically located in Group 4A on the periodic table.

This means that 4 atoms have electrons, and since they have 4 covalent bonds, if the tendency of carbon in a compound is high, it is equated with a high molecular weight.
In addition, elements typically found in organic compounds include H, C, N, O, F, P, S, Cl, Br, and I.
Therefore, if you are introduced to organic chemistry, you can say that it is easier to memorize this level.
Before simply entering organic chemistry, you should briefly learn the terminology and the structure of atoms.
Inductive effect
resonance effect,
steric effect
stereo-specific
chemo-selective
stereo-selective
regio-selective, light-transmissive selection
Degree should go to know the meaning
The structure of the atom is very simple
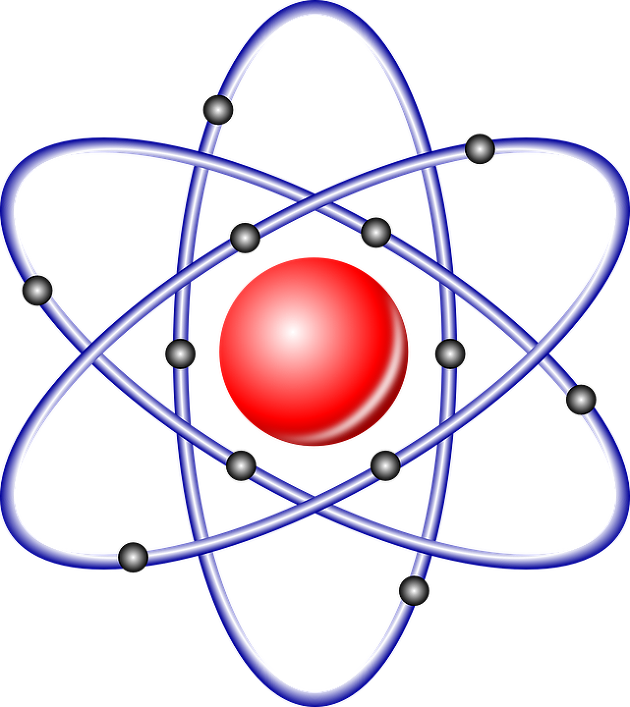
We studied when we were young.

The nucleus is the sum of protons and neutrons, its size is 10^-15m, and the atomic number has the number of protons and isotopes. You only need to know the average atomic weight.
Also, the size of the atom is 2*10^-10m, the size is 200pm, and you only need to know that it is 2Å (Angstrom).
When you get into the orbit function, you have to suffer a lot
There are s, p, d, and f as orbital functions, and the squared ψ^2 of the wave function is called the probability of being found at that place, and it is good to know this much
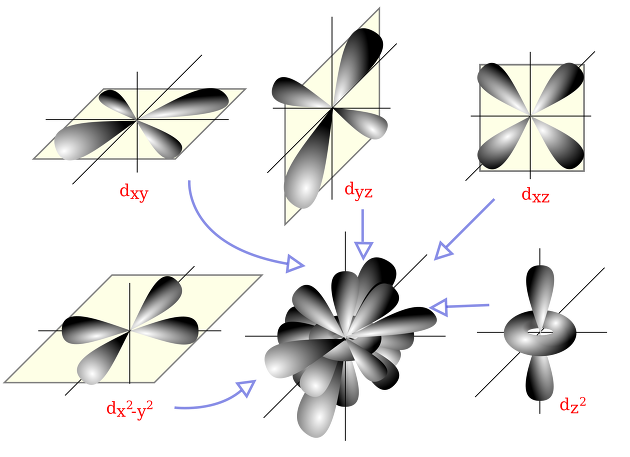
In addition, if it is S, it is round, if it is p, it is a dumbbell type, if d, it is a clover model.
As you enter the electronic layout, you only need to know two principles and one rule: three.
1. It is a stacking principle.
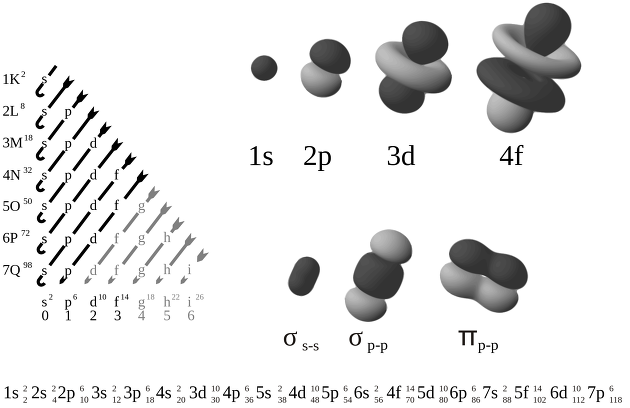
You can see that it is stacked in 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d.
2. Pauli's exclusion principle.
When in one orbit, two electrons enter, meaning each spins in the opposite direction.
3. Hunt's Rule
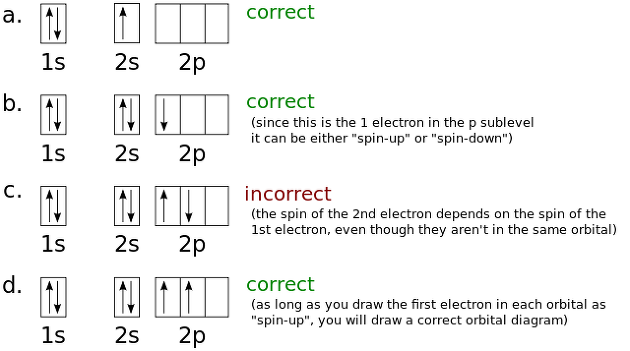
As it is piled up in the order of 1s, 2s stacking principle in stable atom, electrons must first enter 2p, 2py, and 2pz at 2p, respectively, and then 2 must go into opposite spins.
Also, it would be good to know Van't Hoff and Le Bel's three-dimensional tetrahedral structure, octet rules, electrostatic attraction, and covalent bonding.
You only need to know the non-covalent electron pair and the bond formula through the Lewis Braille dot and line bond structural formula to know the difference.

Entering the valence bonding theory (molecular orbital function theory), it seems that you only need to know the degree of cylindrical overlapping (sigma bonding) of hydrogen, which is a great example of overlapping orbital functions.
The most important hybrid orbital function will be explained through Sp3 hybridization in the structure of CH4.

Carbon and C have 1S2,2S2,2P2 orbital functions, so CH4 has the same C-H bond and thus hybridizes.
The + of 2S is the +,- part divided between the nodes in 2P, and it becomes larger by adding to +, and becomes smaller by offsetting from -, resulting in an asymmetric structure.
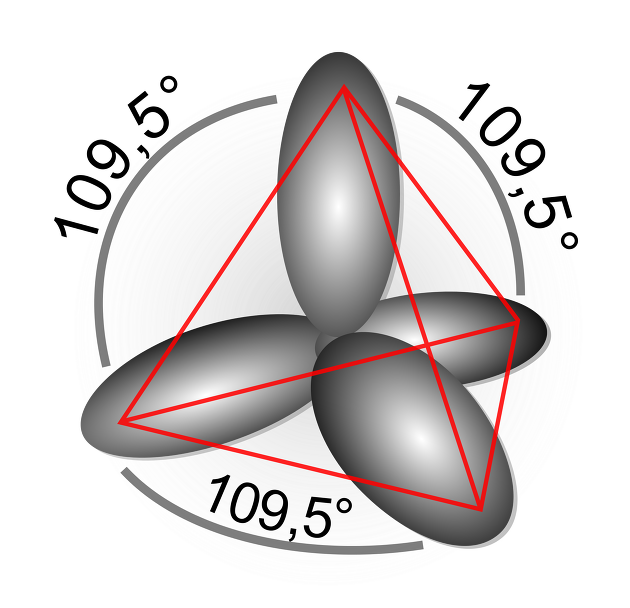
Therefore, it can be seen that the SP3 hybrid orbital function is larger than the S or P orbital function as it overlaps more effectively than other atomic orbitals.
You can see the text translated in korean. : https://biostudy.tistory.com/4
'과학 > 유기화학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Hybrid orbital function and molecular orbital function, structural formula (0) | 2021.01.31 |
|---|---|
| LD50, national health indicator (0) | 2020.08.16 |
| 알켄의 수산화 반응, 환원 산화, 라디칼 첨가 (0) | 2016.05.23 |
| 알켄의 안정성과 방향성, 제조와 반응 (0) | 2016.05.16 |
| 알켄의 불포화도, 명명법, 시스 트랜스 (0) | 2016.05.09 |